What is an IoT SIM Card?
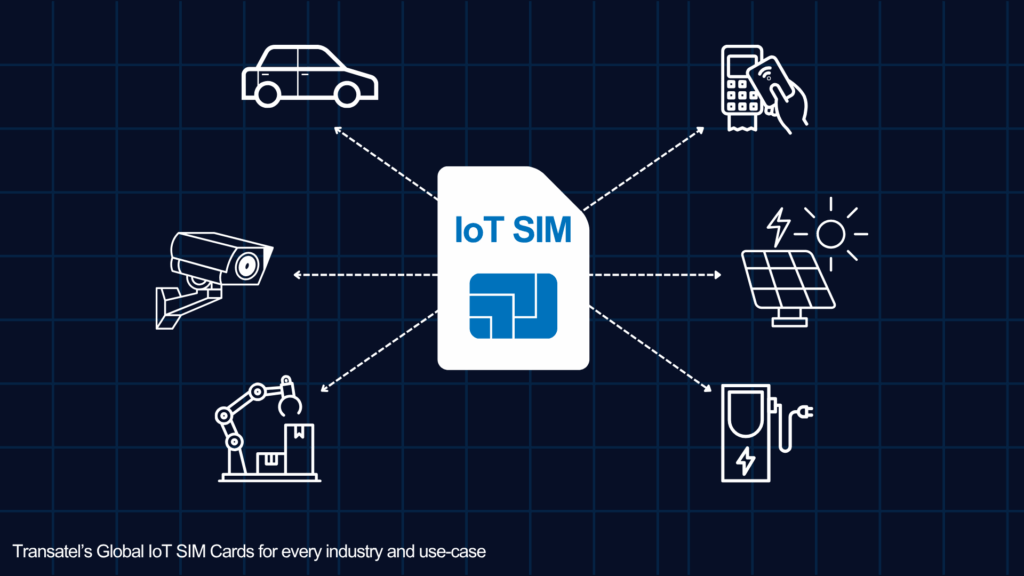
An IoT SIM card is a specialised SIM card created to meet the unique connectivity needs of Internet of Things (IoT) devices such as machines, sensors, cameras and trackers. Unlike the standard SIM cards used in mobile phones, IoT SIMs provide strong, secure and global network access, making them ideal for connected devices operating across different locations and networks.
What is IoT (Internet of Things) though?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of physical objects, things like devices, vehicles, appliances and industrial machinery, that are equipped with sensors, software, and internet connectivity. These smart objects are designed to collect, exchange and act on data, either with each other or with cloud-based platforms.
What are some examples of IoT in action?
- Connected cars can send maintenance alerts straight to your smartphone.
- Wearable health monitors track vital signs and notify healthcare providers if anything seems off.
- Logistics companies use IoT to track shipments around the world and improve delivery routes.
What is the difference between IoT SIM Card & Regular SIM?
| Feature | Regular SIM Card | IoT SIM Card |
| Primary Use | Phones, tablets etc. | IoT devices (sensors, trackers, systems, etc.) |
| Network Access | Usually Single network | With transatel – multi-network |
| Coverage | Standard | Enhanced for remote environments |
| Lifecycle | Shorter (consumer-focused) | Long-term (device lifecycle aligned) |
| Management | Limited | Advanced remote management capabilities |
| Security | Basic | Advanced (VPNs, private APNs, etc.) |
How were IoT SIM cards invented?
The story of IoT SIM cards starts with the original SIM. In 1991, a Munich-based company called Giesecke+Devrient (G+D) created the world’s first commercial SIM card and sent it to a Finnish mobile provider. This tiny chip allowed phones to connect securely to mobile networks, and that same principle still underpins today’s connected devices on the Internet of Things.
In the early days, IoT devices used standard SIM cards designed for mobile phones. But those cards were too bulky and not built for the tough conditions or long-life spans that many IoT devices require, like sensors on remote farms or trackers in shipping containers.
As IoT developed, it became clear that a more specialised solution was needed. New SIM cards had to:
- Fit into compact devices
- Survive harsh environments
- Be managed and updated remotely
- Last for years without physical maintenance
What are the different sizes of an IoT SIM Card?

| Format | Dimensions (mm) | Typical Use Cases | Key Features |
| Mini-SIM (2FF) | 25 x 15 x 0.76 | Vending machines, ATMs, vehicles | Durable, suitable for larger devices |
| Micro-SIM (3FF) | 15 x 12 x 0.76 | Routers, GPS systems, tablets | Space-saving |
| Nano-SIM (4FF) | 12.3 x 8.8 x 0.67 | POS systems, wearables, smartwatches | Ultra-compact, used in modern devices |
| Embedded SIM (MFF2) | 6 x 5 x 0.9 | Drones, industrial sensors, smart meters | Soldered onto PCB, highly durable, supports remote provisioning |
All IoT SIM form factors, ranging from full-size, mini, micro, and nano SIMs to embedded SIMs (eSIMs) and integrated SIMs (iSIMs), can be available in both programmable and non-programmable versions. The key difference lies not in the physical format but in the flexibility of the SIM’s internal configuration.
Programmable SIMs allow remote provisioning and updating of network profiles. This means users or mobile network operators can change or add profiles without physically replacing the SIM. This is especially useful for devices that need to switch networks frequently, such as in IoT deployments, international travel, or enterprise mobility solutions. Programmable SIMs are commonly used in eSIM and iSIM but can also exist in traditional removable formats.
Non-programmable SIMs, on the other hand, are fixed once issued. The network profile is hardcoded and cannot be changed remotely. Any update or change in carrier requires physically replacing the SIM card. While they are simpler and often cheaper, they lack the flexibility and scalability of programmable options.
In essence, regardless of the SIM’s physical size or type, the distinction between programmable and non-programmable lies in how adaptable the SIM is to changing network needs.
Are IoT SIMs the End of Regular SIMs?
IoT SIM cards are not replacing regular SIM cards because each is designed for different needs. Regular SIM cards are made for phones and tablets, mainly for people to call, text, and use the internet. They work well for everyday personal use and are tied to a single network, often with fixed contracts.
IoT SIM cards are built for machines and smart devices that need to send data, sometimes in tough environments or across many countries. They offer features like better durability, longer lifespan, remote management, and global network access, which regular SIMs do not provide.
In simple terms: Regular SIMs are best for people and their phones, while IoT SIMs are made for smart devices and business needs. Both types are useful, but for different jobs, so one does not replace the other.
Final Thoughts on IoT SIM vs Regular SIM
IoT SIM cards connect billions of devices, from smart meters and industrial sensors to autonomous vehicles, to communicate reliably and securely across the globe. Unlike traditional mobile SIM cards, IoT SIMs are purpose-built for long-term deployments, enhanced security, and seamless global connectivity.
This makes it essential for businesses looking to scale their IoT solutions without facing connectivity disruptions or security risks. Partnering with a trusted IoT connectivity provider such as Transatel goes beyond simply acquiring an IoT SIM card.
You gain a global connectivity partner who ensures your devices remain online wherever they operate, whether you are tracking assets across continents, managing fleets, or deploying smart city infrastructure. Investing in the right IoT SIM connectivity solution, with robust security, global coverage, and expert support, sets the foundation for long-term success in the connected world.
Click here to test Transatel’s IoT SIM Card with automatic multi-network switching capabilities.
Regular SIMs are made for phones, you pop them in and out and use them for calls and the internet. IoT SIMs, on the other hand, are built for machines. They’re tougher, last longer, can be managed remotely, and are made to work in everything from smart meters to delivery trucks.
IoT SIMs are designed to survive extreme heat, cold, vibration, and moisture. They also have stronger security features to protect data, since many IoT devices are placed in remote or unprotected locations.
If one mobile network has poor coverage in an area, an IoT SIM with multi-network access can switch to another one automatically. This means your device stays connected, even when it moves across regions or countries.
IoT SIM providers often offer flexible data plans, you can share data across many devices, avoid overage fees, and only pay for what you use. This keeps costs low, especially when you’re running thousands of devices.