eUICC, or “reprogrammable SIM cards”, is a revolutionary technology that allows over-the-air switching of mobile carriers without the physical replacement of the SIM card. In this article, we call it eSIM, which would refer to “embedded SIM” but that the industry often refers to to discuss eUICC, despite being inaccurate. It enables the remote downloading of a new SIM to replace the current one, making eSIM a more flexible and cost-effective way to switch mobile operators, without even physically swapping a SIM card in the device. In this article, we will delve into the evolution of eSIM technology, with a particular focus on the groundbreaking adoption of the SGP .31/.32 eSIM standards that bring significant advantages to Machine-to-Machine (M2M) use cases. We’ll also reflect on the pioneering role of Transatel, a global leader in cellular IoT connectivity, in the development and implementation of eSIM technology.
The consumer perspective of eSIM
For consumers, eSIM technology offers a straightforward and convenient solution. The device, such as a smartphone, tablet, or laptop, fetches a SIM profile from a SIM profiles database via the internet. The mobile operator operates an “SM-DP+”, which lists the SIM cards and stores SIM profiles. The SIM cards operated by this mobile operator may download profile from that mobile operator’s SM-DP+ or from any other one, through the Internet.
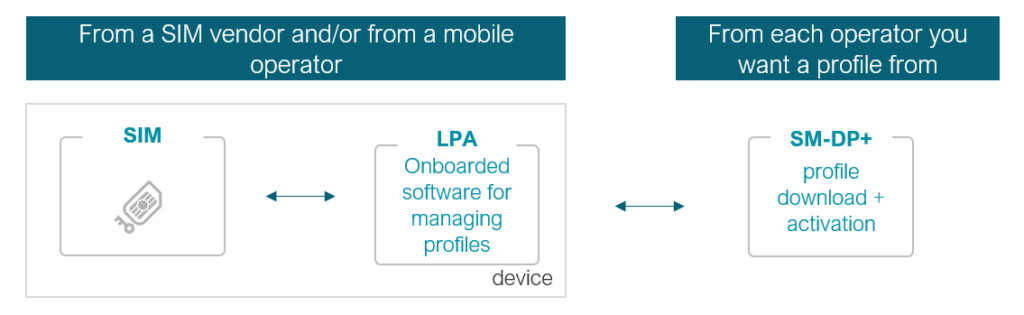
However, there are two key prerequisites for this process:
> The device must have a user interface and a local application (LPA) that triggers the profile download. You can try this on your eSIM-compatible phone, tablet or laptop with Transatel’s Ubigi service.
> Consumer eSIM technology does not support fleet control, thus limiting its applicability in enterprise business or for M2M connectivity.
This is great news for the consumer market, and it is no mistake that Apple has been phasing out physical SIM cards out of its iPhone over the past years. Yet, it does not answer the fleet managers’ needs neither for managing enterprise mobile telephony fleets nor M2M appliances.
Transatel’s breakthrough in 2015: the birth of eSIM in laptops. In 2015, Transatel led the market by equipping Microsoft’s Surface laptops with the first-ever reprogrammable eSIM cards. This marked a significant leap in connectivity technology, transforming the traditional tethered hardware SIM card concept into a reprogrammable, embedded solution within devices. This enabled users to change their network service providers without physically replacing SIM cards, thus breaking down geographic barriers and enhancing consumer freedom.
The challenges of eSIM technology for M2M
For M2M applications, the traditional eSIM technology has been complex and expensive. It requires an “SM-SR” server to function as the “SIM database”. This can be either owned by the mobile carrier or the enterprise (from a SIM vendor). The SM-SR serves as an orchestrator of sorts to send orders such as downloading a profile, but fetching these profiles is troublesome. The SM-SR needs to be interconnected with SM-DPs, that actually store the SIM profiles. Each mobile carrier operates its own SM-DP. This results in having to interconnect the SM-SR with as many SM-DPs as there are mobile carriers the enterprise needs to download profiles from.
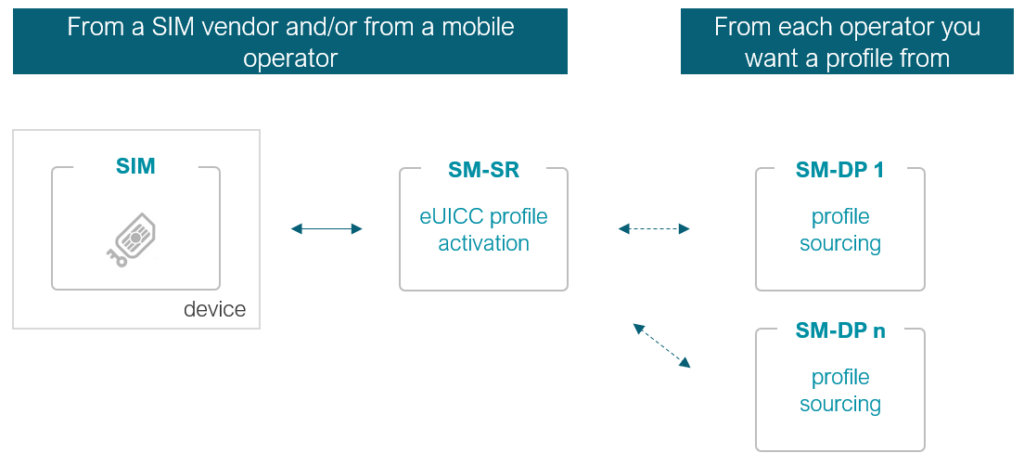
Each of these SM-DP interconnects is costly and requires expert resources. Due to these complexities and high costs, eSIM for M2M was mainly used in large-scale IoT projects where such investments were justifiable. Alas, this does not work for all large-scale IoT projects: this technology does not work for NB-IoT projects.
Transatel, M2M eSIM for a tier-1 aircraft maker. Continuing its pioneering journey, Transatel took another significant step in 2017 by developing M2M eSIM technology for tier-1 aircraft makers. This solution opened new horizons in connectivity for the aviation industry and automotive OEMs. The M2M eSIM technology enabled seamless and robust connectivity between different components of aircraft, paving the way for advancements in safety, efficiency, and the overall flight experience.
The game-changer: SGP .31/.32 eSIM standards
The new SGP .31 / .32 eSIM standards are set to revolutionize the eSIM landscape, particularly benefiting M2M use cases. These standards unify the operations of consumer and M2M eSIMs, drastically reducing costs and complexities.
The key benefits for M2M applications include:
> Simplification of M2M eSIM management, making it as easy as consumer eSIM without the need for interconnection, making eSIM usable for most IoT projects
> Enabling fleet management, a feature that was previously unattainable with consumer eSIM, opening the path for broader B2B mobile telephony adoption.
> Facilitating eSIM profile management for NB-IoT devices, thus broadening the scope for IoT implementation.
By making M2M eSIM projects easier to manage, these standards enhance scalability, making them beneficial for projects of all sizes, and effectively replace the previous, more complex standards.
Transatel, pushing for mass market eSIM adoption for IoT Solution providers. In September 2022, Transatel demonstrated its relentless commitment to innovation. As a result, one of its key clients has been the first to benefit from the new SPG .31/.32 eSIM standard, months ahead of the completion of the standard and its release in April 2023! The adoption of the SPG .31/.32 eSIM standard represents a significant advancement in eSIM technology, delivering superior security, greater flexibility, and enhanced operational efficiency. By adopting this new standard before its formal release, Transatel not only showcased its agility but also its willingness to take calculated risks to stay at the forefront of technology.
Will the new SGP .31/.32 eSIM standards replace the existing eSIM standards?
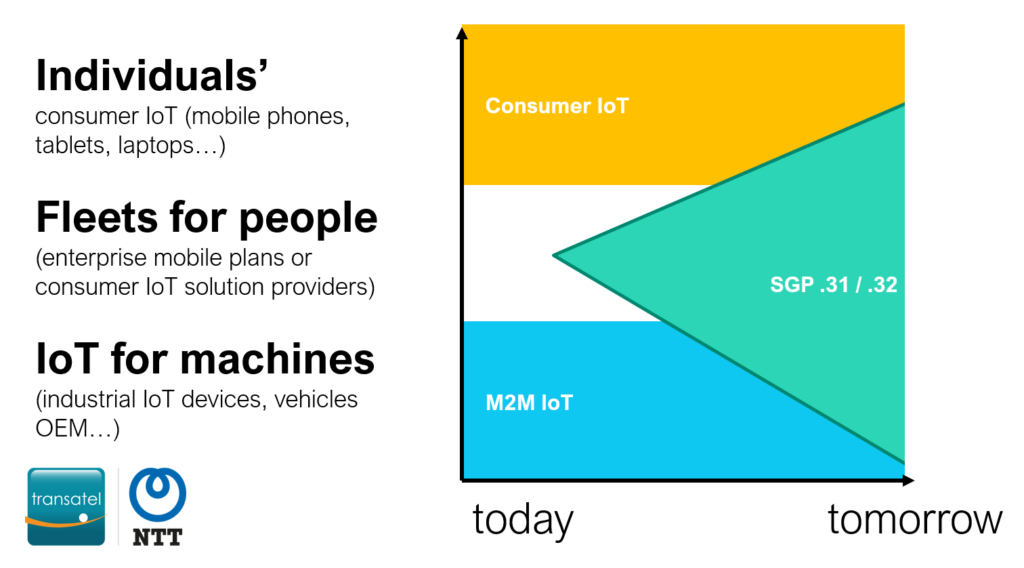
Not fully. This new specification derives from the consumer eSIM standards, adding new capabilities. This makes it relevant to address opportunities that could not before (such as enterprise mobile plans), without replacing the classic end-user requirements.
It facilitates drastically the M2M eSIM standard, thus it is likely to replace the previous M2M standard for most of the new eSIM M2M projects. In select cases, the previous, M2M standard will remain relevant, though we expect it to become marginal. The lack of skills about this standard will probably further reduce its capability to survive this new SPG .31 / .32 standards.
Are the new SGP .31/.32 eSIM standards set to completely displace the existing eSIM standards?
Not entirely. The new SGP .31/.32 specifications are an extension of the consumer eSIM standard, with added capabilities. This expansion in capabilities allows these standards to cater to previously unaddressable opportunities, such as enterprise mobile plans, without supplanting the requirements of conventional end-users: you will still rely on the already existing consumer eSIM standard on your iPhone or Android device when you travel to lower your roaming costs using services like Ubigi.
The SGP .31/.32 standards significantly simplify the M2M eSIM standards, making it probable that they will replace the prior M2M standard for a majority of new eSIM M2M projects. In certain circumstances, the original M2M standard may still hold relevance, though its usage is projected to become peripheral. The scarcity of expertise concerning the old standard could further hasten its obsolescence in the face of the new SGP .31/.32 standards.
eSIM, beyond borders
The journey of eSIM technology has been marked by continuous evolution, with the development of the SGP .31/.32 eSIM standards being a significant milestone. Transatel’s journey echoes this narrative of innovation, from the introduction of the first eSIM in laptops to pioneering the use of M2M eSIM, and being one of the early adopters of the SGP .31/.32 eSIM standards.

Transatel’s pivotal role in this journey has significantly advanced the field of eSIM technology. As we progress towards a more connected future, Transatel’s commitment to challenging and transcending traditional boundaries assures their continued leadership in the eSIM revolution, particularly in the realm of M2M applications, paving the way for a world of seamless connectivity, beyond borders.
Learn more about Transatel’s cellular IoT connectivity solutions and book a meeting with an expert by visiting www.transatel.com/iot/






