Transatel – NTT Research & Innovation Director Romain Durand, recently spoke at the 5G and Beyond conference organized by Mobile Europe. In his talk, he explained how public connectivity is still critical to private 5G & LTE cellular networks and why industries require hybrid connectivity solutions that leverage the best of both worlds.
What’s the difference between Public & Private 5G networks ?
5G is the new and improved version of wireless communication that offers faster data transfer rates, lower latency, and increased connectivity compared to previous technologies. However, it can be deployed either on mobile carriers’ public spectrum or as private cellular networks in factories, campuses, and other industrial facilities.
Public 5G networks are like traditional cellular networks that are open to the public, and anyone with a compatible device can access them. They are operated by Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) and provide coverage across a broad geographic area. The network infrastructure is shared among multiple users, and it is the responsibility of the MNO to maintain and upgrade it regularly. Public 5G networks are suitable for individuals and small businesses that need mobile connectivity on the go.
On the other hand, private 5G networks are essentially local connectivity network for businesses and industries. They offer fast & reliable wireless networks compared to public networks. Private networks provide security and privacy for business data, they also save costs compared to public networks for cellular connectivity especially when dealing with large amounts of data on mobile broadband.
How can businesses leverage Private 5G networks?
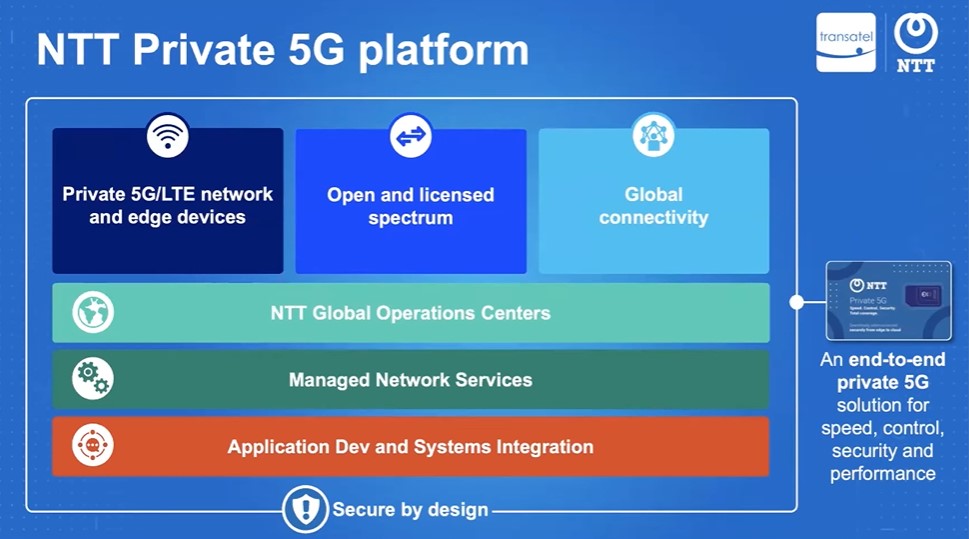
Private 5G networks offer businesses a local connectivity bubble providing high performance, low latency, high bandwidth, and high reliability network on premises. These networks offer security and privacy for business data, particularly in industrial sites or factories where sensitive data is abundant. They are cost effective compared to public networks for cellular connectivity. Mobility and security features make private 5G networks a viable option for businesses and a much better alternative to traditional Wi-Fi connectivity.
However, private cellular networks require a significant investment in equipment and skills, making them a challenge for non-telecom operators. For example, NTT offers Private 5G as a service, a hassle-free network on their premises that lacks necessary skills and equipment to operate.
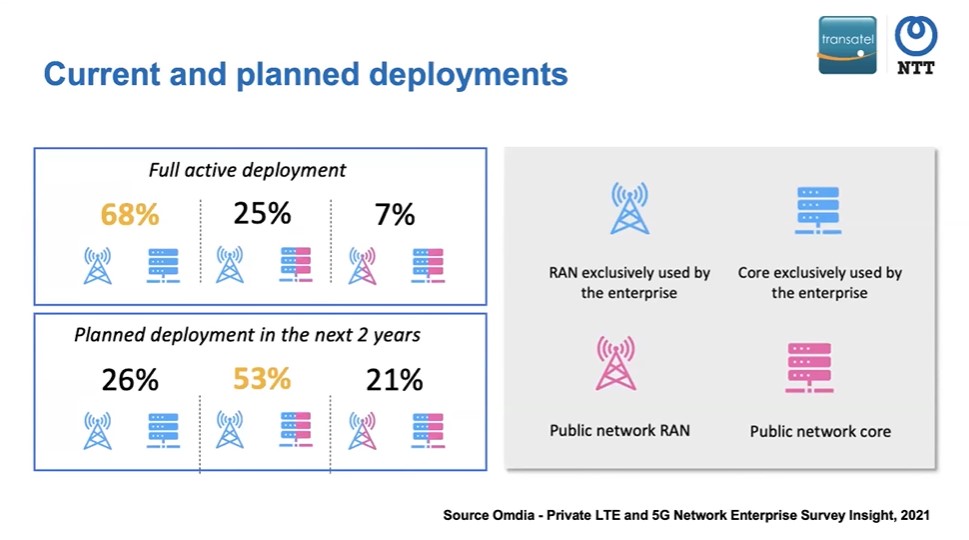
Based on the survey from Omdia, the private network deployments are mainly a standalone network. So, 68% of the standard network deployment are on premises, but there is a trend towards a hybrid solution to combine private and public network components.
How to ensure continuity of service between Public & Private 5G networks?
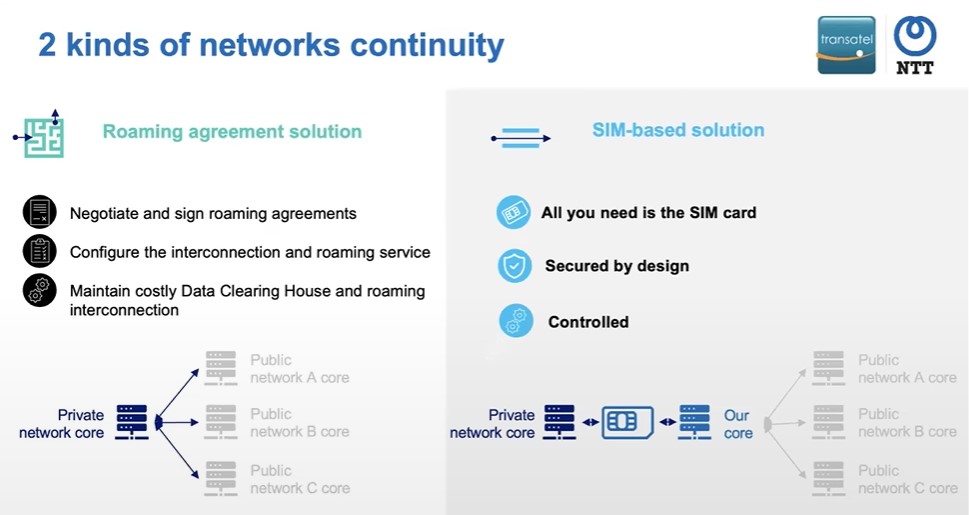
There are two solutions for ensuring continuity between private and public cellular networks. The first is a roaming agreement solution, which involves negotiating and signing roaming agreements, interconnecting with mobile carriers and the switching between private and public networks is controlled. This is achieved by using APIs that are provided by the SIM card to external applications. Different use cases are explored where a controlled switch mechanism is necessary, such as when the private network is unavailable and a backup public network is needed.
However, this can be a difficult process as you are a small network and may not be seen as an attractive opportunity by the public network operators.
Assuming you can sign the roaming agreements, you will then need to interconnect with the mobile operators. This means that your private network must have the roaming functionality, which is not always the case. You may also incur additional costs for third-party services such as GRX providers and Data Clearing houses for billing purposes.
The second solution is a SIM-based solution that provides both access to private and public networks within the SIM card. This solution is secure and controlled, as the private and public networks are separated, and the only linking path is the SIM card. Despite these challenges, it is possible to enable roaming functionality through a roaming agreement.
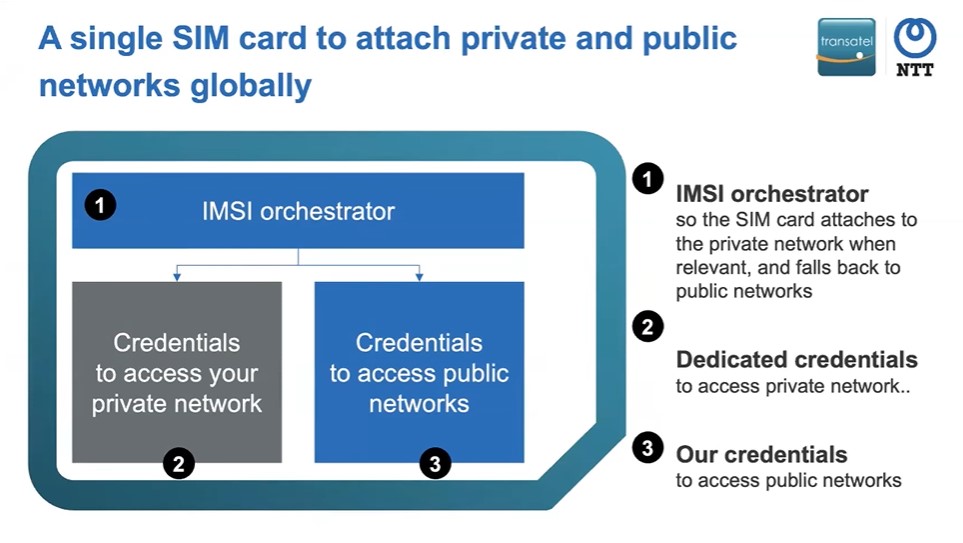
Transatel offers support for this process, we developed an in-house IMSI orchestrator application that manages multiple IMSIs within a SIM card, essentially allowing several lines or several SIMs to be used within the same card. This application facilitates the switch between one IMSI and another, making it easy for users to switch between their private and public networks.
Network continuity and interoperability matters
The roaming in industrial applications remains a challenge to maintain. For example, during flights, Airbus collects data that needs to be transmitted over cellular networks upon landing. Currently, public networks are used for this data transmission. However, due to the increasing demand to connect outside the private 5G network and the availability of roaming in IoT, there needs to be seamless continuity between the private and public 5G networks. To meet this demand, airport priority networks have been deployed worldwide. Another use case is distributed workforces that need to switch seamlessly between private and public networks with the help of GPS location and NFC detection. This allows employees to work on-site and remotely.
The automotive industry currently uses private networks in factories, but faces the challenge of transitioning to public networks for cars on the road. This requires ensuring continuity between private and public networks. In order to address this challenge, car manufacturers are being invited inside GSMA. As a result, we can expect to see an increase in collaborations between the industry and mobile network operators.
The continuity between private and public networks needs to be perfect otherwise, there could be significant trouble for big machines like aircrafts or cars. Public and Private networks have their advantages and disadvantages, and it is essential to ensure continuity between them, particularly for businesses that use private networks on their premises. It will be interesting to see how this trend evolves in the future.
Learn more about Transatel Private LTE / 5G network extension solutions: https://www.transatel.com/iot/private-cellular-networks/